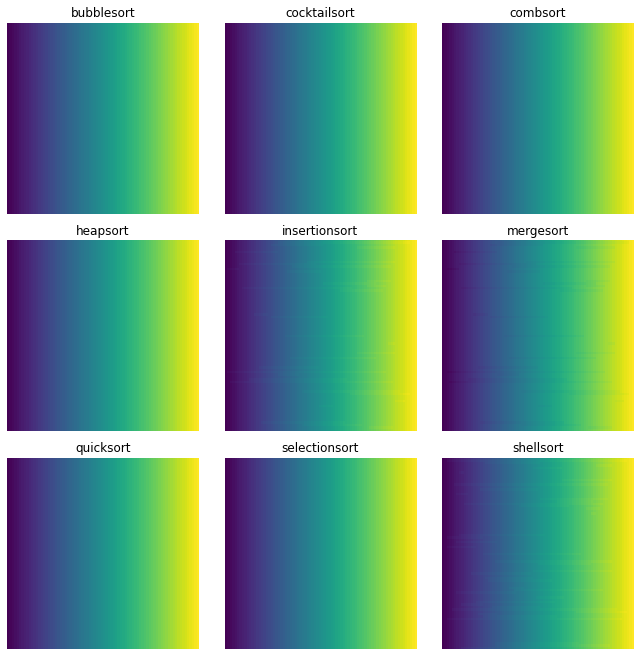Visualizing Sorting Algorithms
Sorting algorithms vary, for example, in their time and space complexity. From an artistic viewpoint, they also vary in the way they transiently reposition the elements of the array as the algorithm progresses. Here, we will animate this transient behavior.
Initial setup
[1]:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import animation
from IPython.display import HTML
Implement sorting algorithms
Each sorting function will be implemented as a generator. This way, each algorithm will track its state implicitly and the resolution can be adjusted freely by positioning the yield calls. In addition, the raw data is mutable and will be passed by reference. Thus no unnecessary copies are made.
[2]:
def bubblesort(array):
n = len(array)
for i in range(n - 1):
for j in range(0, n - i - 1):
if array[j] > array[j + 1]:
array[j], array[j + 1] = array[j + 1], array[j]
yield array
[3]:
def insertionsort(array):
for i in range(1, len(array)):
key = array[i]
j = i - 1
while j >= 0 and key < array[j]:
array[j + 1] = array[j]
j -= 1
yield array
array[j + 1] = key
yield array
[4]:
def selectionsort(array):
n = len(array)
for i in range(n):
min_idx = i
for j in range(i + 1, n):
if array[min_idx] > array[j]:
min_idx = j
yield array
array[i], array[min_idx] = array[min_idx], array[i]
yield array
[5]:
def cocktailsort(array):
n = len(array)
swapped = True
start = 0
end = n - 1
while swapped:
swapped = False
for i in range(start, end):
if array[i] > array[i + 1]:
array[i], array[i + 1] = array[i + 1], array[i]
swapped = True
yield array
if not swapped:
break
swapped = False
end = end - 1
for i in range(end - 1, start - 1, -1):
if array[i] > array[i + 1]:
array[i], array[i + 1] = array[i + 1], array[i]
swapped = True
yield array
start = start + 1
yield array
[6]:
def partition(array, low, high):
i = low - 1
pivot = array[high]
array_list = []
for j in range(low, high):
if array[j] < pivot:
i = i + 1
array[i], array[j] = array[j], array[i]
array_list.append(array.copy())
array[i + 1], array[high] = array[high], array[i + 1]
array_list.append(array.copy())
return i + 1, array_list
def quicksort(array, low=0, high=None):
if high is None:
high = len(array) - 1
if low < high:
pi, array_list = partition(array, low, high)
yield from array_list
yield from quicksort(array, low, pi - 1)
yield from quicksort(array, pi + 1, high)
yield array
[7]:
def mergesort(array, left_index=0, right_index=None):
if right_index is None:
right_index = len(array) - 1
if left_index >= right_index:
return
mid = (left_index + right_index) // 2
yield from mergesort(array, left_index=left_index, right_index=mid)
yield from mergesort(array, left_index=mid + 1, right_index=right_index)
left_copy = array[left_index : mid + 1].copy()
right_copy = array[mid + 1 : right_index + 1].copy()
left_copy_index = 0
right_copy_index = 0
sorted_index = left_index
while left_copy_index < len(left_copy) and right_copy_index < len(right_copy):
if left_copy[left_copy_index] <= right_copy[right_copy_index]:
array[sorted_index] = left_copy[left_copy_index]
left_copy_index = left_copy_index + 1
else:
array[sorted_index] = right_copy[right_copy_index]
right_copy_index = right_copy_index + 1
sorted_index = sorted_index + 1
yield array
while left_copy_index < len(left_copy):
array[sorted_index] = left_copy[left_copy_index]
left_copy_index = left_copy_index + 1
sorted_index = sorted_index + 1
yield array
while right_copy_index < len(right_copy):
array[sorted_index] = right_copy[right_copy_index]
right_copy_index = right_copy_index + 1
sorted_index = sorted_index + 1
yield array
yield array
[8]:
def heapify(array, n, i):
largest = i
l = 2 * i + 1
r = 2 * i + 2
if l < n and array[largest] < array[l]:
largest = l
if r < n and array[largest] < array[r]:
largest = r
if largest != i:
array[i], array[largest] = array[largest], array[i]
yield array
yield from heapify(array, n, largest)
def heapsort(array):
n = len(array)
for i in range(n // 2 - 1, -1, -1):
yield from heapify(array, n, i)
yield array
for i in range(n - 1, 0, -1):
array[i], array[0] = array[0], array[i]
yield from heapify(array, i, 0)
yield array
[9]:
def shellsort(array):
n = len(array)
gap = n // 2
while gap > 0:
for i in range(gap, n):
temp = array[i]
j = i
while j >= gap and array[j - gap] > temp:
array[j] = array[j - gap]
j -= gap
yield array
array[j] = temp
yield array
gap //= 2
[10]:
def stoogesort(array, low=0, high=None):
if high is None:
high = len(array) - 1
if low >= high:
return
if array[low] > array[high]:
array[low], array[high] = array[high], array[low]
yield array
if high - low + 1 > 2:
sep = (high - low + 1) // 3
yield from stoogesort(array, low, high - sep)
yield from stoogesort(array, low + sep, high)
yield from stoogesort(array, low, high - sep)
yield array
[11]:
def combsort(array):
n = len(array)
shrink_factor = 1.3
_gap = n
sorted_ = False
while not sorted_:
_gap /= shrink_factor
gap = int(_gap)
if gap <= 1:
sorted_ = True
gap = 1
for i in range(n - gap):
if array[i] > array[i + gap]:
array[i], array[i + gap] = array[i + gap], array[i]
sorted_ = False
yield array
[12]:
algorithm_list = [
bubblesort,
cocktailsort,
combsort,
heapsort,
insertionsort,
mergesort,
quicksort,
selectionsort,
shellsort,
# stoogesort, # takes a long time
]
Try out one of the algorithms
Let’s see how each generator yields intermediate arrays until it finally sorts it completely.
[13]:
array = np.arange(4)[::-1]
print('Initial array:', array)
for i, arr in enumerate(bubblesort(array)):
print(f'At iteration {i}:', arr)
print('Final array:', array)
Initial array: [3 2 1 0]
At iteration 0: [2 3 1 0]
At iteration 1: [2 1 3 0]
At iteration 2: [2 1 0 3]
At iteration 3: [1 2 0 3]
At iteration 4: [1 0 2 3]
At iteration 5: [0 1 2 3]
Final array: [0 1 2 3]
Create animations
The animate function is straight-forward, it simply updates the data in each plot. The data is updated in the step function. Here, a generator is created for each sorting instance (row of each data block) and then executed until all generators are exhausted.
[14]:
def animate(data_list, im_list):
"""Put each data block in appropriate image."""
for data, im in zip(data_list, im_list):
im.set_data(data)
return im_list
def step():
"""Run algorithms."""
# initialize sorting functions
generator_list = [
sort_function(row)
for block, sort_function in zip(data_list, algorithm_list)
for row in block
]
while True:
has_stopped = 0
for gen in generator_list:
try:
# advance each sorting algorithm by one step
next(gen)
except StopIteration:
has_stopped += 1
if len(generator_list) == has_stopped:
# all lists are sorted when all generators are exhausted
break
# yield intermediate result for plotting of animation frame
yield data_list
def create_animation(array_length, repetition_num, max_iter_num=50_000, block_size=3):
# TODO: get rid of evil global variables
global data_list
# generate unsorted data
block = np.repeat([np.arange(array_length).astype(float)], repetition_num, axis=0)
[np.random.shuffle(row) for row in block]
data_list = [block.copy() for _ in algorithm_list]
# setup figure
size = np.ceil(np.sqrt(len(algorithm_list))).astype(int)
fig, ax_grid = plt.subplots(
nrows=size,
ncols=size,
figsize=(size * block_size, size * block_size),
constrained_layout=True,
)
ax_list = ax_grid.ravel()
im_list = [
ax.imshow(data, interpolation='nearest') for ax, data in zip(ax_list, data_list)
]
[ax.axis('off') for ax in ax_list]
[ax.set_title(alg.__name__) for ax, alg in zip(ax_list, algorithm_list)]
# create animation
return animation.FuncAnimation(
fig=fig,
func=animate,
frames=step, # init_func=init_func, # TODO: use init_func to start with appropriate frame
save_count=max_iter_num,
interval=10,
repeat=True,
fargs=(im_list,),
blit=True,
)
[15]:
%%time
small_animation = create_animation(10, 10, block_size=2)
HTML(small_animation.to_jshtml(default_mode=None))
CPU times: user 6.16 s, sys: 232 ms, total: 6.39 s
Wall time: 6.17 s
[15]:
[16]:
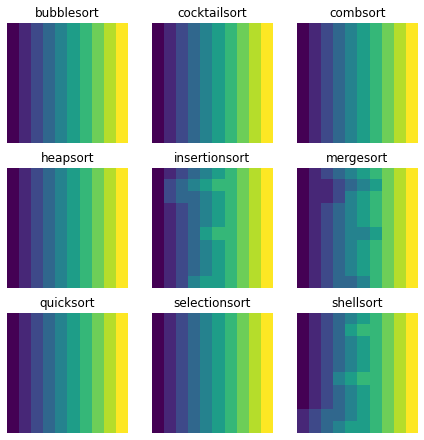
%%time
big_animation = create_animation(80, 80)
HTML(big_animation.to_html5_video())
CPU times: user 17min 41s, sys: 2min 4s, total: 19min 46s
Wall time: 6min 48s
[16]: